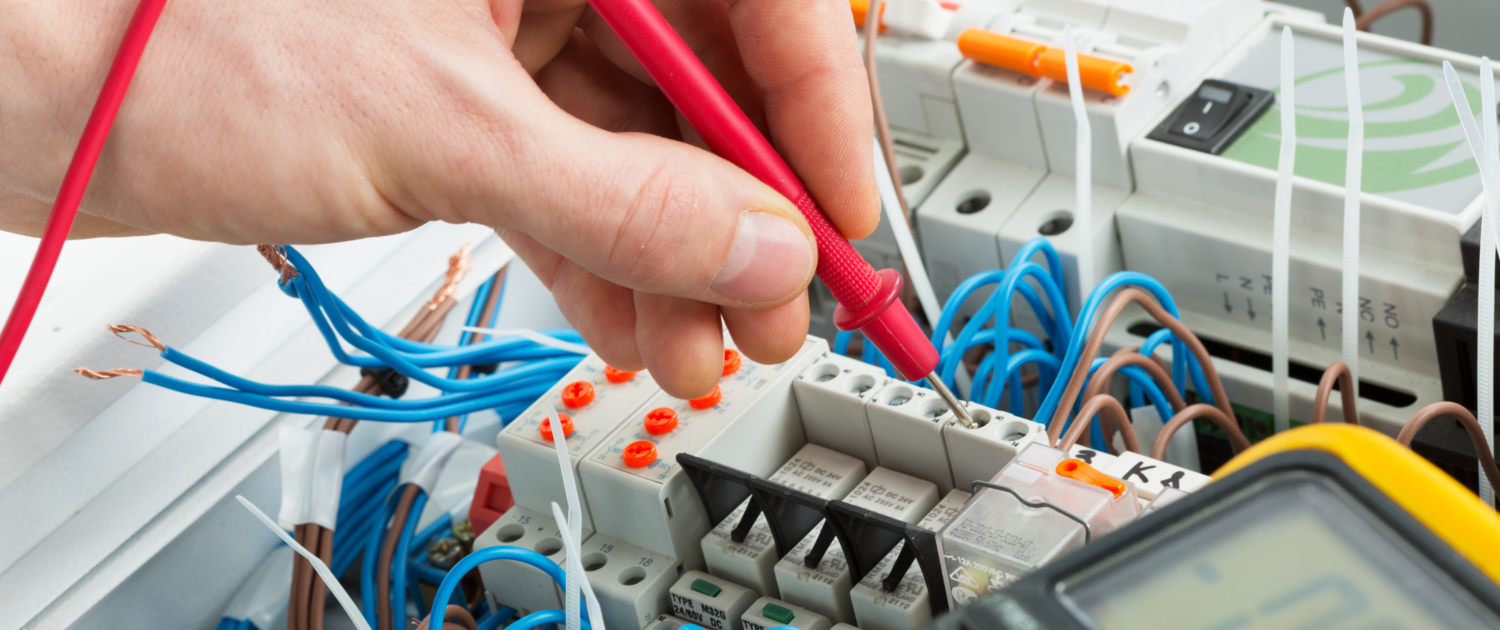
Electrical Installation Tests
Electrical installation tests are an important part of the electrical testing process. There are a number of different types of electrical installation tests, and each one serves a specific purpose. Some of the most common electrical installation tests include insulation resistance testing, continuity testing, and ground fault circuit interruption (GFCI) testing.
Performing regular electrical installation tests is an important way to ensure the safety of your home or office. If you are not sure which tests need to be performed, or if you need help performing them, it is best to consult a professional electrician. They will be able to help you ensure that your electrical system is safe and up to code.
Continuity testing
This type of testing is used to test whether two points in an electrical circuit are electrically connected. Continuity should be present in all electrical circuits to ensure that electricity can flow through them as intended.
Insulation resistance testing
Insulation resistance testing is used to test the electrical insulation of a device or circuit. The test measures the resistance of the insulation between two points. Insulation resistance should be as high as possible to prevent electricity from leaking out and causing a fire or other hazard.
GFCI testing
GFCI testing is used to test for ground faults. A ground fault is a situation where electricity flows outside of the intended path, often resulting in an electrical shock. This test helps to prevent these dangerous situations from happening.
Electrical Installation Tests (Pat Testing)
What is PAT Testing?
PAT testing is a safety inspection of portable electrical appliances and equipment. The acronym PAT stands for Portable Appliance Testing. During a PAT test, an electrician will inspect your devices for any signs of wear and tear or damage that could lead to an electrical accident. They will also check the plugs, cables, and fuses to ensure they are in good condition.
When Should I PAT Test my Electrical Devices?
Generally, you should PAT test your electrical devices annually. However, the frequency of PAT testing may differ depending on your specific circumstances. For example, if you work in a high-risk environment, you may need to PAT test your devices more often. However, the frequency of PAT testing may differ depending on your specific circumstances. PAT testing is not a legal obligation in the United Kingdom, but it is recommended by Health and Safety regulations.
How are PAT Tests conducted?
Pat tests involve a few simple steps. An electrician will start by inspecting the cables and appliances visually for any damage, such as exposed components or split cables. Provided that the appliance passes the visual test, an insulation test is then carried out. This measures the condition of the insulation that protects any part of the appliance that carries a current.
Lastly, an earthing continuity test is then carried out. The purpose of this test is to determine if the earthing conductors are sufficient to protect users against electric shock. If everything checks out, the electrician will give the all-clear for the appliance to be used.
What are the Benefits of PAT Testing?
There are many benefits to PAT testing your electrical devices. Some of the key benefits include:
- Ensuring your electrical equipment is safe to use
- Reducing the risk of electrical accidents
- Meeting Health and Safety regulations
Electrical Installation Tests (EICR)
An Electrical Installation Conditioning Report is an inspection of an electrical installation to ensure that it is safe and meets the requirements of the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989. The report will identify any deficiencies and make recommendations for corrective action. It is usually carried out by a qualified electrician.
What is the purpose of an Electrical Installation Conditioning Report?
- identify any deficiencies in the electrical installation.
- make recommendations for corrective action
- ensure that the electrical installation meets the requirements of the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989.
While the standard recommendation for an EICR test is every 5 years, higher risk environments require much regular testing, between 1-3 years depending on the premises. Below are some examples of high risk
- Industrial Units – 3years
- Areas of public entertainment – 3 years
- Leisure centres, Spar hotels – 3 years
- Cinema – 1 year
- Caravan Park – 1 year
- Marinas – 1 year
- Petrol Stations – 1 year
EICR Report
The report will usually include the following
- a description of the electrical installation
- an assessment of the electrical installation safety
- a list of any deficiencies in the electrical installation
- recommendations for corrective action.
An Electrical Installation Conditioning Report should not be confused with a PAT test. A PAT test is a safety inspection of electrical appliances and equipment to ensure that they are safe to use. If you are in any doubt about the safety of your electrical installation, you should consult a qualified electrician.
Other Common electrical testing procedures
Protective Conductor Continuity
A protective conductor continuity test is a simple, yet important, electrical test that can be used to ensure the safety of an electrical installation. The purpose of this test is to verify that there is no break in the circuit between the point of protection and the point of use. This type of test is often used when verifying the installation of arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs).
To perform a protective conductor continuity test, you will need to use a voltmeter. First, disconnect the power to the circuit you are testing. Next, use the voltmeter to measure the voltage between the point of protection and the point of use. If there is no break in the circuit, the voltage reading should be the same at both points. If there is a break in the circuit, the voltage reading will be different at each point.
It is important to note that this type of test should only be used as a preliminary check. For a more accurate assessment, you should also test the impedance of the protective conductor.
Circuit Breaker Functionality Test
A circuit breaker is an electrical device that is used to protect your home from overloads and shorts. By tripping the breaker, it prevents any further electrical current from flowing through the circuits. This can save your home from a potential fire.
It is important to ensure that your circuit breaker is functioning properly. To do this, a qualified electrician will need to test the circuit breaker by opening and closing it several times. An electrician may use the following steps to check the circuit breakers functionality.
- Open the circuit breaker box and locate the circuit breaker that you want to test.
- Turn off the power to the circuit breaker by flipping the switch to the “off” position.
- Close the circuit breaker by flipping the switch to the “on” position.
- Wait a few seconds and then open the circuit breaker by flipping the switch to the “off” position.
- Repeat steps 2-4 several times to test the circuit breaker’s functionality.
Ring Circuit Testing
There are a few different types of electrical installation tests that can be performed in order to ensure the safety and proper function of an electrical installation. One common type of test is the ring circuit test.
A ring circuit, also known as a loop circuit, is a type of electrical wiring configuration in which all the sockets in a room or building are connected in a loop. This type of circuit is typically used in homes and small businesses, and is considered to be safer than other wiring configurations because it helps to prevent the build-up of electrical sparks that can lead to fires.
In order to test a ring circuit, you will need to use a multimeter. Set the multimeter to the “resistance” setting, and then touch the probes to the two terminals on each socket. The multimeter should read infinity if the circuit is open, or zero if the circuit is closed. If you get a reading somewhere in between, then there is a problem with the circuit.
Polarity Testing
Another common type of electrical installation test is the polarity test. This test is used to verify that the voltage in a circuit is flowing in the correct direction. In order to perform this test, you will need a multimeter set to the “voltage” setting. Touch the probes to two terminals on a socket, and then look at the reading on the multimeter. If the voltage is flowing in the correct direction, the reading will be positive. If the voltage is flowing in the wrong direction, the reading will be negative.