Differences between Cat5 and Cat6?
Cat5 and Cat6 are both types of Ethernet cables, these cables are very similar in many ways, but they have different capabilities. For most applications cat5 or cat5e will be sufficient. However, with the advancement of technology you may find yourself looking for a solution that can handle more data or has a faster connection. The logical approach is of course to look at the next available category of data cables. In this article we will look at the differences between Cat5 and Cat6 and whether you need to upgrade.
Key differences between Cat5 and Cat6 cables
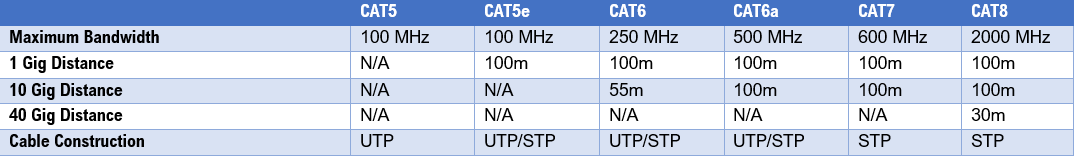
- Cat6 cables use four pairs for data transfer instead of two, meaning that the signal is transferred up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbps)
- Cat6’s with 100Base-TX connector connects more efficiently to computers and other devices
- Cat5e has a cable diameter approximately 20% smaller than cat6
- Cat6a is the only cable that can support 10GBASE-T (10Gbps Ethernet) over 100 meters
- Cat6 is more expensive than cat5e by about 15% per cable length.
- Cat5 can only handle data speeds up to 100Mbps (100 megabits per second) while Cat6 cable offers significantly faster speeds of up to 10Gbps (10,000 megabits per second).
- Latency is the time it takes for a data packet to travel from one point to another. Cat6 cables have lower latency than cat5 cables.
- Cat6 cables are also more resistant to crosstalk and interference than cat5 cables. Crosstalk is the bleed of signal from one wire to another, and interference is outside signal sources (like an electrical cord running parallel to the Ethernet cable) that can disrupt or distort the signal.
- Cat6 cables can be used in a variety of applications, including telephony, home entertainment and network storage
- Cat5 cables are limited to just one-way communication, while Cat6 cables can support two-way communication. This means that with Cat6, you can use your cable as both a transmitter and receiver, which can be handy in some situations.
Construction of the data cable
There are several key differences between Cat5 and Cat6 cables. The most obvious difference is in the size – Cat6 cables are around 20% larger in diameter than Cat5 cables. This is due to the fact that Cat6 cables have a tighter twist, which helps to reduce interference between cores. Additionally, Cat6 cables have a central plastic separator which splits the 4 pairs of cores into their own section. This helps to further reduce interference and crosstalk. Overall, these differences make Cat6 cables a better choice for high-speed data applications.
Although the size increase of 20% doesn’t sound like much if you’re installing 1 or 2 cables. The increase will become more noticeable when installing hundreds of cables. You will need to reconsider the containment required, tray work and conduits may need to be increased.
Difference between Cat5e and Cat6 Bandwidth Capability
The fundamental difference between Cat5e and Cat6 is in the bandwidth capability. Cat5e is only rated for Gigabit Ethernet (1000Mbps) while Cat6 is rated for 10-Gigabit Ethernet (10,000Mbps). This means that if you have a 10GbE network, Cat6 cables are the only option.
However, for most applications Cat5e or Cat6 will be more than sufficient.
The other main difference between Cat5 and Cat6 cables is in the crosstalk and interference performance. As we mentioned earlier, Cat6 cables have a tighter twist and a central separator which helps to reduce interference. Additionally, Cat6 cables are shielded which helps to protect against outside interference. This makes Cat6 cables the better choice for high-speed and high-traffic networks.
There are a few situations where you might need Cat6 cables. If you are setting up a 10GbE network, or if you need the best possible performance and interference protection, then Cat6 is the cable for you. Otherwise, Cat5e is a more than adequate choice for most applications.
Difference between Cat5 and Cat6 material cost
There is a big difference in the cost of Cat5 and Cat6 materials. Cat5 is less expensive than Cat6 because it uses thinner gauge wire and doesn’t require as much insulation. Cat6 is more expensive because it uses thicker gauge wire and needs more insulation to protect the data signals from interference.
Cat6 cables are more expensive than Cat5 cables by about 15% per cable length. This is due to the fact that Cat6 cables have a tighter twist, which helps to reduce interference between cores. Additionally, Cat6 cables have a central plastic separator which splits the 4 pairs of cores into their own section. This helps to further reduce interference and crosstalk. Overall, these differences make Cat6 cables a better choice for high-speed data applications.
Other related articles – What is PoE?