Alternating Current or Direct Current?
Which is Safer; Alternating Current (AC) or Direct Current (DC)?
Read on in this article where we compare AC vs DC and their differences. When you’re working with electronic products it’s crucial that you understand the difference between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). Not only will this knowledge allow you to work on these products with a firm understanding of how they operate electrically, but it will also provide you with a vital level of safety. The greater you understand the difference of DC vs AC the better decisions you can make
Electricity, after all, is a natural form of energy and one that can be highly dangerous when not treated carefully or with respect. Therefore, to help keep you safe and expand your understanding of electricity, we’re going to look at AC vs DC before explaining which one is safer.
Difference Between AC vs DC
AC and DC are, as their names suggest, both types of electrical currents and they’re differentiated by the directional flow that each one takes. To understand these in more depth, we’ll dig a little deeper into exactly what they are:
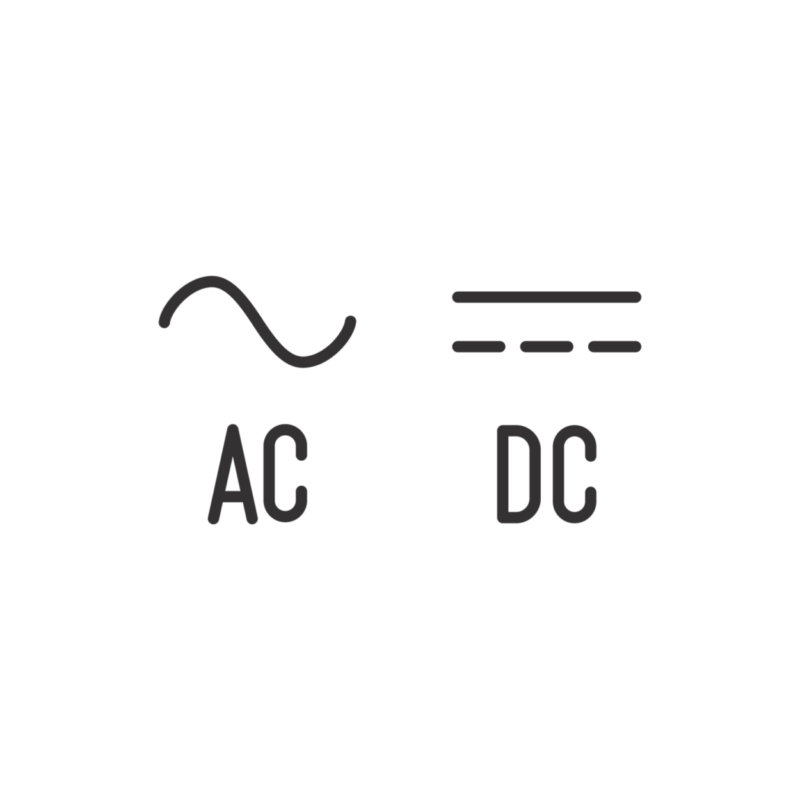
-
Alternating Current:
This form of electrical current can reverse the direction of its flow – hence the alternating title – and it’s this versatility which makes it perfect for delivering electrical power to homes and businesses. For example, if you’re using a television at home then it’s running off AC and if you’re using a photocopier at work then, again, it will be using AC.
-
Direct Current:
An electrical charge which moves in only one direction, DC tends to flow through conductors, semi-conductors and insulators. The most common usage of DC is in batteries as a power supply for electronic devices, but DC also has a use in remote generation sites where it can be used to transfer power in large amounts.
Now you understand a little more about these two electrical currents, it’s time to investigate the dangers they present and which one is safer.
Safety Aspects of AC and DC
Regardless of which current you’re working with, both AC and DC are highly dangerous elements to be working with. Thus, both have the potential to cause you serious harm. Humans haven’t evolved to cope with the effects of electrical currents being applied to the body. Therefore, this can result in mild electrical shocks that make you jump all the way through to heart attacks and death.
Whilst both currents are dangerous, AC is considered the more dangerous current to be working with due to the following reasons:
- The human body has a higher impedance to DC currents than AC, so this means that humans are able to withstand the effects of an electric shock arising from DC exposure much better than when exposed to AC.
- Experiments have demonstrated that it’s easier to let go of live parts of a DC circuit than observed in AC circuits. Naturally, this makes it significantly easier to reduce the impact of exposure to electricity when working with DC compared to AC.
- An electric shock has the capacity to induce ventricular fibrillation which can lead to heart failure and death. Avoiding any form of electric shock is preferable, but DC is considered safer in these circumstances as the human body’s threshold to DC is considerably higher than to AC.
Safety, as ever, is paramount when working with electricity and, whilst DC is considered safer, it’s essential that all safety precautions are adhered to in order to prevent a serious injury.
We hope you have enjoyed this article comparing AC vs DC
For further articles please visit our Electrical Installation Services Blog Here